Future English and Chatbots
Virag Rohitkumar Shah
Founder, Byte-Man.com
{shahviru4you}@gmail.com
Abstract. Chatbots are computer programs equipped with artificial intelligence & natural language processing algorithms that simulates and processes human conversation to understand what a human wants, and guides them to their desired outcome with as little work for the end user as possible. On the other side, English language is truly the language of international business in today’s world. This paper shows how these two (AI Chatbots & English) have been evolved over time and how their evolution is going to disrupt the customer conversations through the dialogue flow.
Introduction
Every industry is focused on customer needs and experience. Using Machine Learning and Natural Processing Language, AI bots are successful in creating a more human-like response that’s in line with the customer queries. Recently, chatbots received an increased attention from businesses to save 3 things: Time, Money & Manpower.
On the other hand, English is currently the most common language on the Internet Not only AI, internet has also spawned the English Language revolution, the likes of which have never been seen before such that many people, instead of just greeting “Good Morning” use its acronym “gm” during texting. Non-native speakers are also blending it with their mother tongues to create hybrid versions of English, eg. Hinglish (Hindi and English). Example, in Hinglish chat; 9kri means – नौकरी – “Naukri”(meaning ‘Job’). In Guja̩lish(Gujarati and English) chat; 6 means – છે – “Che” (meaning ‘Have’) There’s no denying that the Internet has changed how we write.
Evolution of English
English is arguably the global and most influential language in today’s world. However it contains many vagaries and annoying inconsistencies. Its’ evolution has been somewhat chaotic, absorbing and assimilating many different other European languages and dialects, as well as languages from around the Old British Empire, most notably Hindi.
Below flow chart shows how it has evolved.
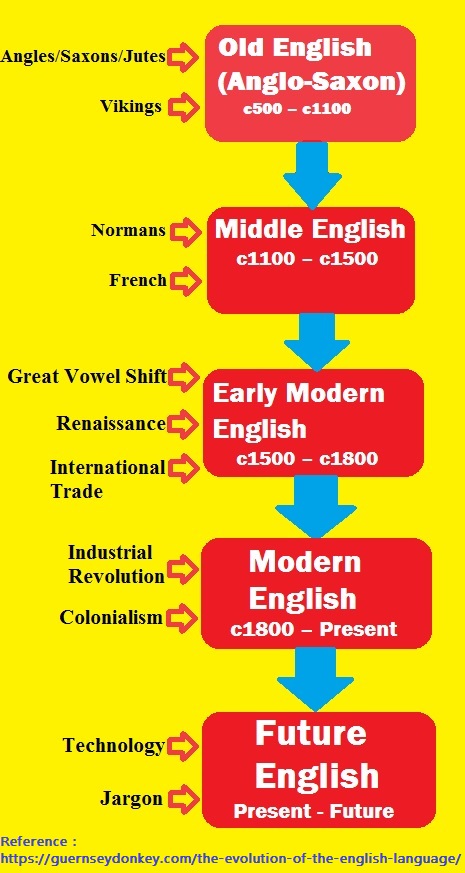
Source: The Evolution of the English Language
Evolution of Chatbots
1950 – THE TURING TEST
The Turing test was developed by Alan Turing for determining whether a machine can ’think’ like a human
1966 – ELIZA
MIT computer scientist Joseph Weizenbaum at the published ELIZA, a program for mimicking human conversation by matching user prompts to scripted responses – it was able, at least for a time, to pass the Turing test, meaning that it fooled humans into thinking they were conversing with a person.
1972 – PARRY
PARRY, written by psychiatrist Kenneth Colby, was intended to converse like a paranoid schizophrenic. It was more serious and advanced than ELIZA and had better underlying approach.
1988 – JABBERWACKY
British programmer Rollo Carpenter created JABBERWACKY, a bot aiming to simulate natural chat in an interesting, entertaining and humorous manner.
1991 – Dr.SBAITSO
Creative Labs developed an artificial intelligence speech synthesis program named Dr.SBAITSO for MS-DOS-based personal computers.
1994 – THE TERM “CHATTERBOT”
Michael Maudin coined the term “ChatterBot”.
1995 – A.L.I.C.E.
Richard Wallace developed Artificial Intelligence Markup Language (AIML) forming the foundation for Artificial Linguistic Internet Computer Entity (A.L.I.C.E.)
2001 – SMARTERCHILD
SMARTERCHILD, an intelligent bot that was available across SMS and messaging platforms, with features such as quick data access and fun personalized conversation, was developed by ActiveBuddy.
2006 – WATSON
IBM introduced WATSON, named after IBM’s first CEO, Thomas J. Watson. Initially it was designed as question-answering computer system specifically to take on human contestants on the game show Jeopardy! Now WATSON uses natural language processing and machine learning to reveal insights from large amount of data.
* 2010 – 2015 BEGINNING OF VIRTUAL ASSISTANTS
Kindly note: Virtual assistants are capable of voice interaction rather than just text & they are programmed to receive, recognize and respond to voice command.
2010 – SIRI (APPLE’S VIRTUAL ASSISTANT) LAUNCHED
2012 – GOOGLE NOW (GOOGLE’S VIRTUAL ASSISTANT) LAUNCHED
2015 – ALEXA (AMAZON’S VIRTUAL ASSISTANT) LAUNCHED
2015 – CORTANA (MICROSOFT’S VIRTUAL ASSISTANT) LAUNCHED
2016 – MESSANGER BOTS
Facebook launched a Messenger platform which allows developers to create interactive bots on Facebook Messenger platform. Within the first two months, more than 10,000 bots were available.
2016 – ZO
Zo, developed by Microsoft, was an English language social chatbot which interacted with human users on an emotional level that can make engagement more enjoyable. It was the successor to the chatbot Tay, which was shut down. Similar counterparts were already available or launched later in India (Ruuh), Japan & Indonesia (Rinna) and Xiaoice (China) by Microsoft.
2017 – WOEBOT
Woebot developed by Woebot Labs is an AI-enabled therapy chatbot designed to help users learn about their emotions with intelligent mood tracking.
English for Online Chat
Millennials (aka Gen Y – born in the 1980’s and 1990’s) and Generation Z (aka Gen Z – born between 1996-2010) users have created a new rulebook for a variant of written English unique to social media. (If you have noticed, here I use aka – an abbreviation for ‘also known as’)
Some new rules for online chat
- Phrases are often abbreviated into one or two syllable words, such as GM (“Good Morning”), GN(“Good Night”).
- Words are shortened by cutting off the rest of the letters, such as Please(“Plz”), Because(“Bc”)
- Words themselves are shortened to just one syllable by cutting off the rest of the word, such as You(“U”), Are(“R”).
- Words are shortened by adding numbers and cutting off some letters, such as Great(“Gr8”), Right(“R8”)
- Replacing entire words by numbers, such as For(“4”), To(“2”)
Future Dialogue Flow

Millennials’ Incorrect English Dialogue Flow as shown in above image Is Converted into Simple English Dialogue Flow
Human – Good morning. How are you?
Chatbot – Good morning. I am fine. How many fight tickets do you want to book?
Human – Three for me. New York to Los Angeles. Tonight.
Chatbot – Your tonight’s 3 tickets are confirmed for New York to Los Angeles.
Human – Great. Thanks. See you later.
Chatbot – You are welcome. Have a safe journey.
Now, some may argue that chatbots should also reply in Millennials & Gen Z’s English version rather than formal one. But as per my opinion it would be better if the English language of the chatbot is formal one because the different abbreviations have different meanings in different cultures.
Spending Power of Y & Z
Marketers have been putting a lot of time and attention on targeting Millennials (Gen Y) and Gen Z as they have more spending power. As per data published by MarketingCharts.com in February 2019; Gen Z (under the age of 25) makes the most transactions annually, at 358 on average, followed by Millennials with 330 on average transactions.
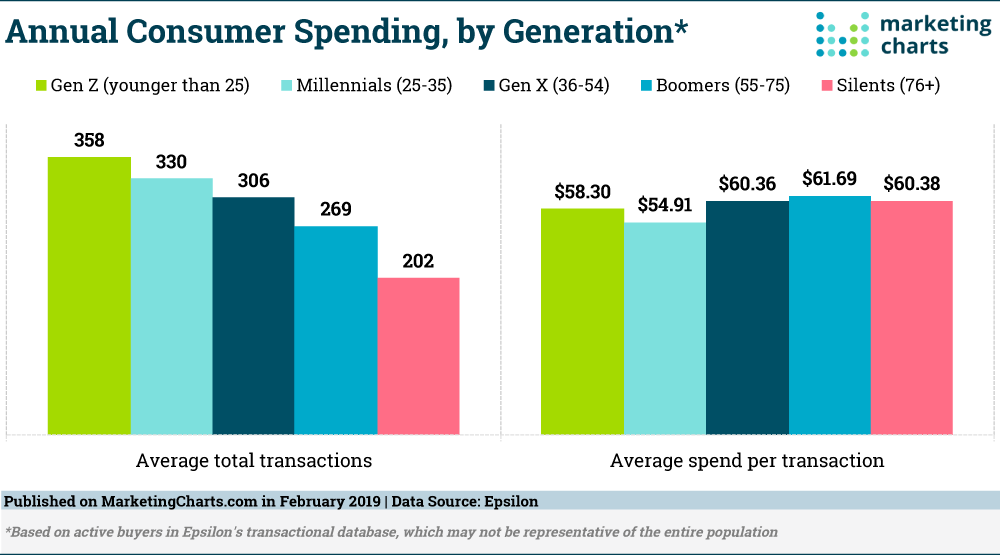
As per Business Insider India January 2020, Gen Zers have a spending power of over $140 billion.
Conclusion
Today businesses need the chatbots those understand the brand-new English dialects of online communities, especially Gen Z & Gen Y who accumulate more spending power. With new technology and advancements being made every few years, Chatbots and English both are expected to evolve more in future and will reshape the user experiences and conversations together.
References:
The Evolution of the English Language (https://guernseydonkey.com/the-evolution-of-the-english-language/)
Chatbot – Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chatbot)
How the Internet Has Changed the English Language by Yahoo Small Business (https://smallbusiness.yahoo.com/advisor/resource-center/internet-changed-english-language-160050172/#:~:text=The%20Internet%20is%20also%20preserving,have%20never%20been%20seen%20before.)
Millennials destroyed the rules of written English – and created something better (https://mashable.com/2018/04/02/millennials-written-english/)
Who’s Spending Their Money? Some Surprising Answers (https://www.marketingcharts.com/customer-centric/spending-trends-107347)
Gen Zers have a spending power of over $140 billion, and it’s driving the frenzy of retailers and brands trying to win their dollars (https://www.businessinsider.in/entertainment/news/gen-zers-have-a-spending-power-of-over-140-billion-and-its-driving-the-frenzy-of-retailers-and-brands-trying-to-win-their-dollars/articleshow/73706715.cms)